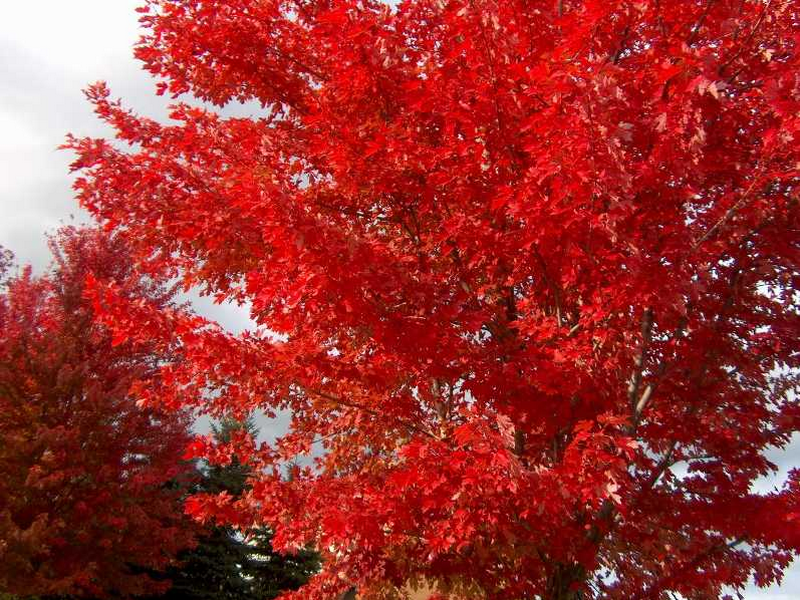
Red Maple Tree
Acer rubrum
Click here to download a PDF of this plant information page (for printing).

Sun Exposure: Sun, Part Sun
Season of Interest: Spring, Summer, Fall
Bloom Time: N/A
Bloom Color: Fall foliage is Red
Height: 40 to 120 ft.
Spread: 30 to 50 ft.
Spacing: 50 ft.
Water Needs: Average
Maintenance: Prune for shape
Soil Type: Clay, Loam, Sandy
Soil pH: Acidic, Neutral
Soil Drainage: Well drained
Pests: Bag worms
Diseases: Canker, Fungal leafspot
Wildlife: Bees, Birds
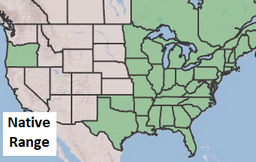
Description:
The red maple is named for its red flowers, red fruit, red twigs, and, of course, its brilliant red or orange fall foliage. They are fast-growing trees that autumn sightseers of the eastern deciduous forest praise for its striking scarlet leaves.
Red maples are perhaps the most abundant tree in the eastern deciduous forest. This status can be attributed to the tree’s ability to tolerate a wide range of habitat conditions and use many different types of resources. Red maples do well in sunny or shady spots, dry or wet soil, and high or low elevation. However deep, moist, acidic soil results in the healthiest trees.
Small red flowers appear on red maples early in spring from March to April, and the seeds develop from April to June. The seeds are often referred to as whirlybirds because the 'wing' shape makes them spin when they fall from the tree. By tree standards, red maples don’t live very long. The average lifespan is only 80 to 100 years. The red maple is one of the maple species whose sap is used to make maple syrup. The biggest syrup provider though is the sugar maple, though, which is named for the high sugar content of its sap. For more information see:
plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/acer-rubrum
Care and Growing Tips:
The red maple is relatively easy to care for and does well throughout all seasons. It does best in well-drained, sandy, loamy acidic soil. Trees growing in alkaline soil will yield pale leaves and suffer stunted growth.
Red maples prefer moist soil but will grow in dry soils provided adequate watering during extreme drought conditions. Once planted, ensure the soil remains moist for the first summer. Fertilization is usually unnecessary, but a general-purpose fertilizer applied in spring is sufficient if needed. The best fertilizers for red maples are rich in nitrogen. Use a three-inch layer of mulch around the tree's base to help the soil hold moisture.